

In 2025, organizations across industries must prepare for a wave of new compliance challenges...

Hiring from anywhere in the world helps companies access wider and more diverse talent pools, but it also introduces challenges related to data privacy compliance.
Failure to comply with data privacy regulations can lead to fines, reputational damage, and loss of customer trust. Learn more about the complexities of data privacy compliance when conducting global hiring.
Key Takeaways
|
Personally identifiable information (PII) refers to any data that can be used to identify an individual — including their name, date and place of birth, Social Security number, or even their email address. Employers have a responsibility to protect employee PII, as such information can be used by malicious actors for identity theft or fraud. Such events can harm the affected individual and the company.
Data privacy compliance helps companies fulfill their legal obligations. But when companies protect employee PII, they also maintain public trust, employee privacy, and their reputation.
Failure to comply with data privacy laws can have severe consequences, including financial penalties, reputational damage, and legal action. Noncompliance can erode employee trust, leading to decreased morale and productivity.
Companies can prioritize data privacy by implementing robust data protection measures and incorporating privacy considerations into their global hiring practices.
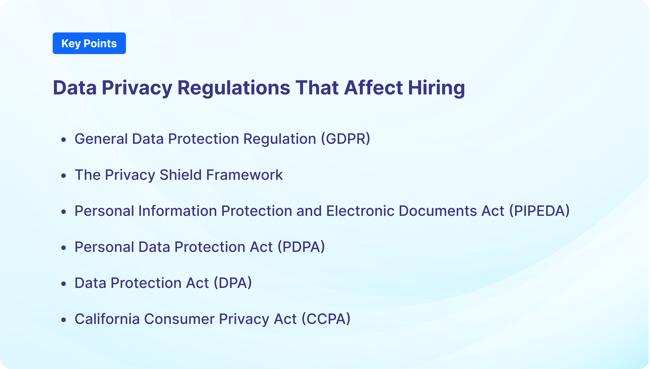
Data privacy regulations have evolved in recent years, with numerous countries, regions, and other jurisdictions implementing data-protection laws. These regulations aim to protect the privacy rights of individuals, and they impose obligations on businesses that handle sensitive personal information, including during the hiring process.
GDPR applies to all organizations processing personal, sensitive data of individuals within the European Union (EU). It governs data collection, processing, storage, and transfer, and provides individuals with extensive rights regarding their personal data.
Under GDPR, companies must obtain consent from individuals before collecting and processing their personal data. Companies must implement appropriate security measures to protect data from unauthorized access or disclosure.
The Privacy Shield framework is a legal mechanism that regulates the transfer of personal data between the EU and the United States. It was created as a replacement for the Safe Harbor framework, which was invalidated by the European Court of Justice in 2015 for not providing adequate protection for EU citizens' personal data.
PIPEDA is a data-protection law that applies to organizations in Canada. The law regulates the collection, use, and disclosure of personal data, and requires organizations to obtain consent from individuals before collecting their personal information. PIPEDA also imposes data security requirements on organizations to protect personal data from unauthorized access or disclosure.
The PDPA sets standards for the collection, use, disclosure, and protection of personal data in Singapore. Organizations’ responsibilities include obtaining consent from individuals before collecting their data, maintaining data accuracy and security, and limiting data retention and transfer. Organizations must also provide individuals with access and correction rights, and notify them about data breaches.
DPA is a data-protection law that applies to organizations in the United Kingdom. Individuals have the legal right to know how their personal information is being used. They must also be able to access and correct their data, ask for its deletion or restriction, and object to certain uses. The law requires organizations to use personal data fairly, lawfully, and with appropriate security measures in place.
The CCPA is a data privacy law that applies to businesses operating in California or that collect personal information from California residents. Consumers have the right to know what personal information is being collected, the right to opt out of the sale of personal information, and the right to delete such information. The CCPA also requires businesses to protect consumer data from unauthorized access or disclosure.

Protecting data privacy during global hiring can be a complex and demanding task. Here are a few of the challenges to data privacy you might encounter when hiring across borders.
Employers hiring in multiple countries could face different legal systems, languages, and regulations in each jurisdiction, making it challenging for companies to devise universal policies for data privacy. This can lead to unintentional non-compliance and potential legal consequences.
Data privacy regulations can have varying standards when it comes to protecting personal data. These variations include the definition of “personal data,” consent requirements, and procedures for handling and transferring data. Companies hiring globally should ensure that they are meeting the most stringent requirements to avoid noncompliance across jurisdictions.
Additionally, companies must have systems in place to manage employee data across different jurisdictions, which can be complex and time-consuming.
Data breaches can occur for many reasons, including cyberattacks or human error. One potential consequence of a data breach is compromised candidate and employee data.
Among the challenges with preventing data breaches is ensuring proper training on data privacy policies and procedures. Cultural and language barriers can pose challenges in this regard, creating gaps in security and increasing the risk of an incident.
Global hiring often involves working with third-party vendors and partners, increasing the risk of data breaches through the sharing of sensitive information. These vendors can have varying levels of security protocols and practices, making it challenging to maintain consistent data-protection measures.
Most data regulations give candidates the right to access their personal data, and companies must be able to quickly and securely grant this access. This can be time-consuming, especially if data is difficult to access or scattered across systems and formats.
Third-party contractors in the hiring process increase the risk of employee data privacy violations. Employers need to thoroughly investigate the vendor's history, reputation, and past compliance practices to ensure that they meet all legal and regulatory requirements.
Doing this due diligence, however, can be challenging for employers because of the time and research involved. This burden increases if your organization is using multiple vendors.

To safeguard PII during and after the hiring process, employers need robust data-protection measures. Here are some best practices that help you protect candidate and employee PII, build trust, and maintain compliance.
A trustworthy background screening partner ensures that all necessary checks and verifications are conducted in accordance with local laws and regulations. A secure platform ensures that sensitive candidate information, including personal and financial details, is protected from unauthorized access.
A global background screening platform should follow consistent screening standards across all countries and jurisdictions. This contributes to fairness and consistency in the hiring process. With a secure platform, employers can access background check results in real time, reducing the time and effort involved in screening candidates. This enables a quicker and more efficient hiring process.
Strong data security measures help protect employee PII and keep organizations in compliance. Your data security strategy also helps establish trust with candidates, employees, and international partners and clients. Lack of security, however, can weaken or jeopardize business relationships and market success.
Regular security audits and ongoing employee training on data protection further enhance the organization's security posture.
When building job descriptions, be clear about the essential qualifications and skills for the position. This will help determine what information, including PII, is relevant and necessary during the hiring process.
Communicating to candidates why this information is needed and how it will be used. This keeps organizations in compliance, demonstrates transparency, and can increase trust in the hiring process.
Periodically review and update your data privacy policies, especially as they relate to the hiring process. This is necessary to keep up with evolving laws and regulations, as well as data privacy best practices
Start with an audit of existing policies and procedures. Look for potential gaps or other areas of improvement. Review areas such as consent forms, data retention policies, and data access controls. These audits can be handled internally or externally.
After identifying changes, communicate them to stakeholders, including HR and hiring managers. This can be done through training sessions or by sharing updated policies and other documents.
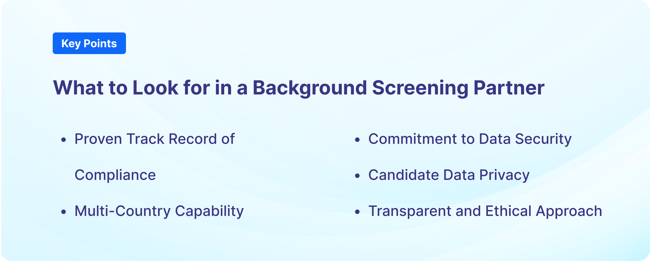
When choosing a background screening partner, consider these key factors to improve data privacy compliance during global hiring.
Select a partner with a proven track record of adhering to data privacy regulations and industry standards throughout the hiring process.
A trusted partner helps protect companies from legal and reputational risks and ensures that background checks are accurate and reliable. Vendors with a strong record of compliance, accuracy, and performance inspire confidence in their services.
Given the global nature of hiring, choose a partner that can conduct background checks in multiple countries. They should have a thorough understanding of the data privacy laws and regulations for each jurisdiction where they operate.
A vendor with multi-country capability can provide comprehensive and reliable background checks while navigating a patchwork of local laws and regulations. Having one trusted partner for multiple jurisdictions helps to mitigate risks and ensure a thorough, consistent screening process for all candidates.
Look for a partner that employs robust data security measures, such as encryption, access controls, and regular security audits. They should be able to demonstrate how they protect employee PII from unauthorized access.
By choosing a vendor with a strong commitment to data security, organizations can ensure that sensitive information is handled responsibly and protected from potential breaches.
Choose a partner that respects and protects employee data privacy. They should have clear, easily accessible policies showing how they collect, use, store, and dispose of employee data.
Failure to properly safeguard candidate data can result in privacy breaches and other incidents, along with legal and reputational consequences for all parties.
A reputable background screening partner should operate with transparency and integrity. They should be open about their data privacy practices and willing to provide detailed information about their background screening processes and regulatory compliance measures. Such partners follow ethical standards and respect privacy rights.
Third-party background screening vendors that offshore the screening process, for instance, may put data privacy compliance at risk because they are subject to different laws and regulations in the country where the screening is being conducted. This can lead to potential inconsistencies and noncompliance, as well as a lack of transparency and control over how personal data is being handled and protected.
Additionally, the transfer of personal data to a foreign country may increase the risk of data breaches and unauthorized access to sensitive information.
Working with a trusted partner like Cisive can help companies maintain a compliant global background screening process, protect sensitive information, and mitigate risks.
Cisive's extensive experience and expertise in global employment screening make them the ideal partner for any company looking to protect data privacy during the hiring process. With their platform-neutral and mobile-enabled technology, Cisive streamlines the screening process, reducing applicant inquiries and providing a seamless candidate experience.
In a world where data privacy is increasingly important, partner with a company that prioritizes compliance and has a proven track record of success. Cisive's configurable and compatible solution is tailored to meet the unique needs of every client, ensuring the protection of their business and the privacy of their employees.
Want to learn more? Schedule a call with one of our background screening experts.

In 2025, organizations across industries must prepare for a wave of new compliance challenges...

As healthcare institutions continue to embrace technology and digitization, the risk of data...

You've probably felt the pressure to hire quickly. At the same time, you’re managing interviews,...